Understanding the Significance
The Helix test specifically simulates the autoclave's performance when sterilizing hollow loads. It focuses on two critical aspects:
1. Evaluating Pre-Evacuation and Steam Penetration
The test assesses the efficiency of pre-evacuation, which is essential for ensuring the complete penetration of steam into the cavities of instruments. Proper sterilization hinges on this crucial step.
2. Monitoring Temperature and Steam Pressure
The Helix test also measures temperature and saturated steam pressure values during the sterilization process. These parameters are essential for effective sterilization.
Applicability
It's important to note that the Helix test can only be conducted in autoclaves equipped with a class B cycle, which includes a fractionated vacuum.
In the field of dentistry, the Helix test takes on particular significance due to the widespread use of hollow instruments. These instruments can be classified into two types:
Type A: Small devices like tips and turbines.
Type B: Cannulas and tubes.
Type B autoclaves are required for sterilizing these instruments effectively, allowing steam to penetrate the cavities, even when they are wrapped.
Adhering to Standards
To ensure the correct operation of an autoclave, the EN 13060 standard recommends performing several tests:
- Vacuum Test
- Bowie and Dick Test
- Helix Test
These tests are conducted before utilizing the autoclave. Additionally, chemical controls (sterilization indicators) and biological controls are carried out during the sterilization cycle to verify the achievement of sterilization parameters.
The EN 13060 standard specifically designates the Helix test as a qualification test for verifying the sterilization capability of Type A hollow bodies (such as turbines and contra-angles).
The Helix Test Procedure
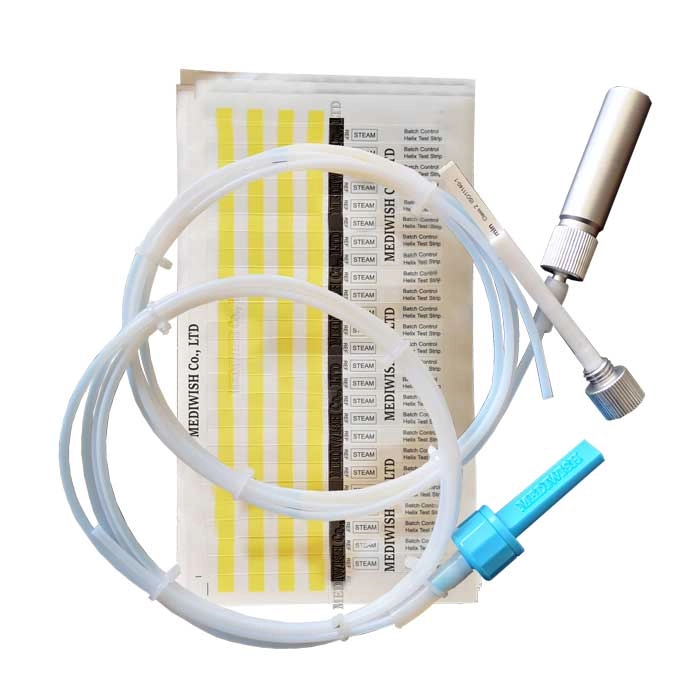
The Helix test is executed after the first empty autoclave loop has been completed. Here's an overview of the procedure:
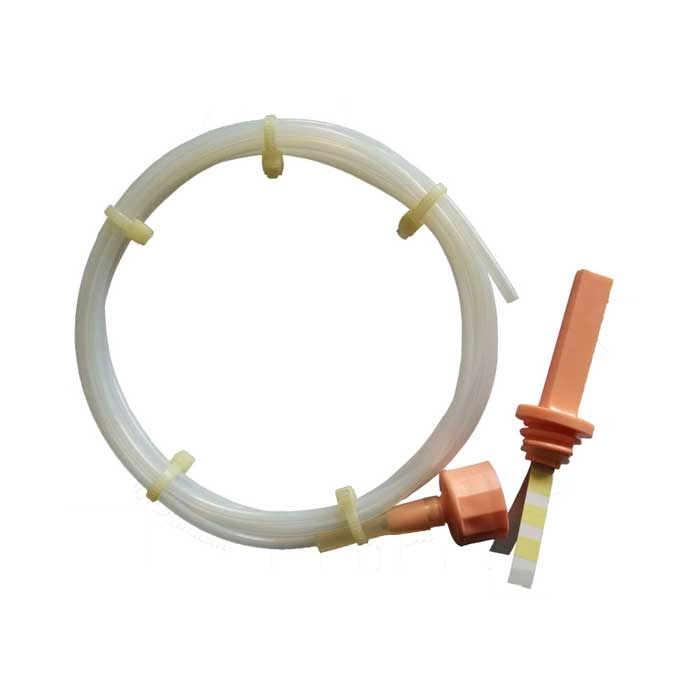
2. Chemical Tracer: A chemical tracer is injected into a capsule connected to a 1.5-meter-long tube, simulating the cavity of a dental instrument.
3. Creating a Vacuum: To ensure the test's success, all air must be removed from the entire tube, creating a vacuum.
4. Introducing Steam: Steam is then introduced to test the autoclave's sterilization ability.
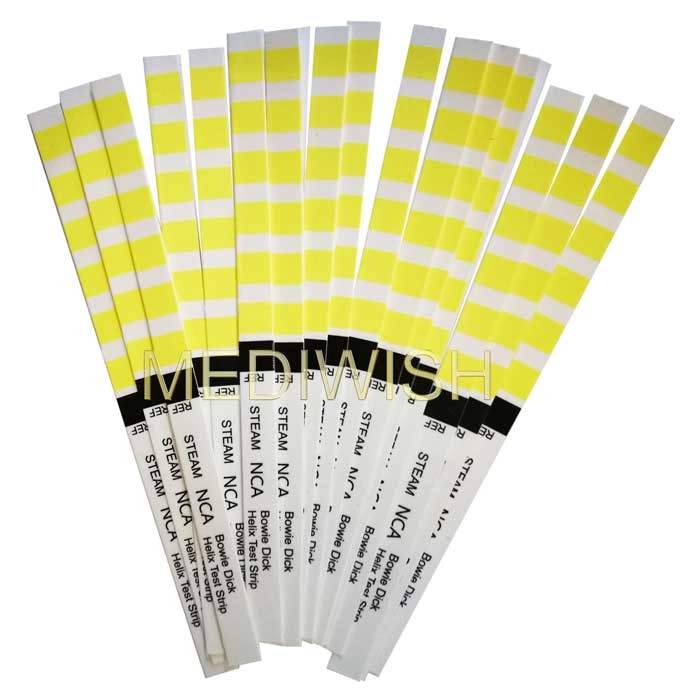
5. Color Change Indicator: The sterilizing agent's contact with the indicator causes a color change, indicating the sterilization process's effectiveness.
If the Helix test yields a negative result, it suggests that steam penetration was suboptimal, and the sterilization process was not successful. In such cases, the test should be repeated, and if the result remains negative, the autoclave should be repaired or replaced.
Ensuring Traceability
Conducting a Helix test daily offers invaluable insights into your autoclave's performance and the effectiveness of instrument sterilization. This data becomes especially crucial if a patient infection occurs. To maintain traceability, it's recommended to maintain a register that includes the indicator's information and printouts of each cycle. This ensures that you can always demonstrate the correct functioning of your autoclave.
Conclusion
The Helix test is an indispensable quality control measure for autoclaves, particularly in dental settings where the sterilization of hollow instruments is essential for patient and staff safety. Regularly conducting this test and maintaining records is critical for ensuring the reliability of the sterilization process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why is the Helix test important in dental offices?
The Helix test is crucial in dental offices because it assesses the effectiveness of sterilizing hollow instruments. Inadequate sterilization can pose risks to both patients and dental staff.
2. What types of instruments fall under Type B autoclaves?
Type B autoclaves are designed to sterilize instruments with cavities, including cannulas and tubes, even when they are wrapped.
3. How often should the Helix test be performed?
It's recommended to conduct the Helix test daily to ensure ongoing monitoring of autoclave performance and sterilization effectiveness.
4. What should be done if the Helix test results are negative?
A negative result indicates suboptimal steam penetration and unsuccessful sterilization. In such cases, the test should be repeated, and if the result remains negative, the autoclave should be repaired or replaced.
5. Why is traceability important in relation to the Helix test?
Maintaining traceability through records and documentation is crucial in case of patient infections. It allows for the demonstration of the autoclave's correct functioning and the effectiveness of sterilization processes.